SAPTA DHATU IN LIVING CELL
According to Ayurveda, all living beings are composed of Dosh, Dhatu, and Mala. Doshas are the biological forces that, control the physiological activity of the living beings. Dhatu makes the anatomical structure of the body and Malas are the excretory waste
formed during various physiological activities. Ayurveda describe somatic structure (Cell and Tissue) as Dhatu. The word ‘Dhatu’ is a Sanskrit word implies for to hold or construct. The whole somatic body is constructed from Dhatu. These dhatu are classified into seven types as per their function. They are- Ras, Rakta, Mansa, Meda, Asthi, Majja and Shukra and their functions are respectively -Nutrition, promotes life, Cover, Lubrication, Hold, Feel up and reproduction. This sapta dhatu concept in Ayurveda is for all living beings unicellular and multicellular animal.
Dhatu (Somatic structure) Multi cellular Function Uni cellular
Ras Body fluid Prinan (Nourishing) Proto plasma
Rakta Blood (Cellular part) Jeevan (Sustain Life) Mitochondria
Mansa Skin & Muscles Lepan (Cover) Protein part of Plasma membrane
Meda Subcutaneous tissue Sneha (Lubrication) Lipid part of Plasma membrane
Asthi Bones Dharan (Hold or give frame work) Endoplasmic reticulum
Majja Bone marrow Puran (To fill up) Ribosome
Shukra Reproductive cell Garbha utpadan (Reproduction) Nucleus
Ras is the first structural constituent its function is prinan means nurturing. It is in liquid form and it gets nourishment from digested ingested food. It is in liquid form so it can reach up to each and every cell of the body giving nourishment to the whole body. It is all ways in constant motion to perform its nourishing work so in Ayurveda Rasa is defined as ah ah gachhati iti Rasa it means the thing in constant motion. We know that body fluid forms the cell bed in the body through which each and every cell of the body get nourishment. The cell does not get nourishment directly through blood but blood releases nutritive material in this cell bed and from here cell get their nourishment. So body fluid in multicellular and protoplasm in the unicellular living body is Rasa dhatu. In multicellular body fluid is divided into two parts one forming the bed of the cell and other running in close vessels pumping through the heart to the whole body. In Ayurveda Heart is said to be the central place of the Rasvah Srotas. Heart propels ras dhatu throughout the body through different circulatory system. The channel through which ras dhatu flow in the body is called Rasvah srotas.
Rakta Dhatu is the second anatomical constituent and its function is Jeevan (promoting life). This function is done by grasping oxygen from lungs and carrying it to the cell bed, from where it is absorbed by the cell and utilize it for oxidation of glucose and generating energy that is utilized during various actions of the body. At the same time, it absorbs carbon dioxide from the cell bed and carries it to the lungs from where it is released out. In Ayurveda, oxygen is named as Ambar Pyush which means nectar of sky. This function is done by hemoglobin so the hemoglobin is the Rakta Dhatu. Liver and spleen are said to be the central place of Rakta Dhatu channel. As per modern science liver and spleen plays important role in formation and destruction of hemoglobin. It means cellular part of blood is the Rakta dhatu according to Ayurveda. In a unicellular organism, mitochondria are the rakta dhatu.
Mansa Dhatu is the third anatomical constituent and its function is lepan means covering. It means muscles which plays a major role in the covering of all body parts of the body is Mansa dhatu. In Ayurveda, its said Manso Balam means strength comes in the body through Mansa i.e. muscles. In unicellular plasma membrane is the Mansa dhatu.
Meda Dhatu is the fourth anatomical constituent and its function is snehan means give lubrication to the body and protect vital organs from shock and injury. The Adipose and fatty tissue lies below skin and muscles are the Meda dhatu. Vapavahanum i.e. Omentum is the root place of the meda dhatu as we see omentum contains a large amount of fatty tissue to protect visceral organ. In unicellular lipid part of the plasma membrane is medo dhatu.
Asthi Dhatu gives framework or particular structure to the body its main function is Dharan means give the framework. Skeletal system gives framework so it is the Asthi dhatu. All the vital organs are protected by the bony structure of the body.in unicellular endoplasmic reticulum gives the structural framework to the cell.
Majja Dhatu is the sixth constituent its main function is puran means filling. Bone marrow fills the hollow parts of the bone so bone marrow is the majja dhatu. As brain and nerves are covered in a bony cage so these cells also comprise in Majja Dhatu as per Ayurveda. In unicellular ribosomes found in the endoplasmic reticulum is the majja dhatu
Shukra Dhatu is the seventh anatomical constituent its function is garbhotpadan means reproduction. So reproductive cells i.e. sperm and eggs are the Shukra dhatu. In unicellular nucleus comprises of DNA and RNA are the Shukra Dhatu.
This way we can explain sapta dhatu of Ayurveda in the modern contest.
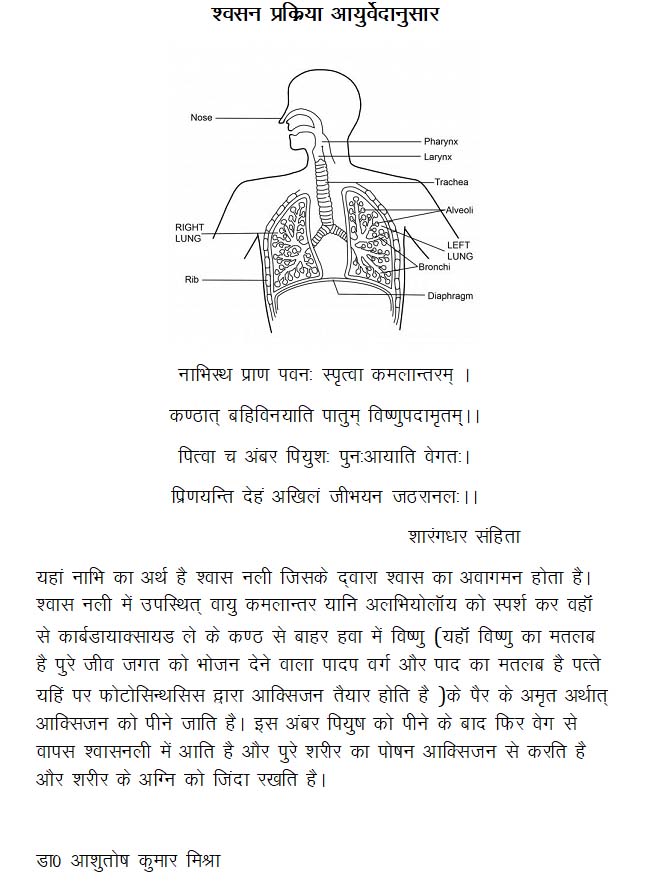
What Ayurveda Says about respiration
The complete breathing process is explained in one of the ancient Ayurvedic text SHARANDHAR SAMHITA by this shloka (Rhymes)-
NAVYASTHA PRAN PAWANAH SPRISTWA HRUD KAMAL ANTRAM
KANTHAT BAHI VINIYARTI PATUM VISHNU PADAMRUTAM
PITUA CHA AMBAR PYUSHAM PUNAH AYATI VEGTAH
PRINAYAN DEHAM AKHILAM JEEVYAN JATHRANALAM
To understand the proper meaning of this shloka it is important to know the meaning of words in English
- Navi means naval but in this context, it is used for the central place of the respiratory system i.e. Bronchial tree
- Pran pawanah means air present in lungs which is the carrier of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- Hrud Kamal Antram means alveoli which are the junction place of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood i.e. pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein comes from the heart, one brings blood from the heart and another takes blood towards the heart.
- Kantha means Larynx
- Vishnu Pad Amrutam means Oxygen. Here Vishnu word is used for the plant. As per Hindu, Vishnu is one of the ditties who nourishes the whole world. Likewise, the plant traps the energy from sunlight and nourishes the whole animal kingdom. So the plants are called autotrophs. Vishnu pad means leg of plants i.e leaf because the root is the mouth of a plant. As we know Oxygen is produced in plant leaf during the process of photosynthesis.
- Amber pyush also means Oxygen. Meaning of Amber is Sky and the meaning of Pyush is nectar. The Ozone layer act as a reservoir of Oxygen in the environment.
- Prinayan means nourishing.
- Deham Akhilam means the whole body.
- Jeevyan Jathranalam means to maintain a livelihood and ignite the digestive fire. This Jatharanalam is also be understood in another way that Oxygen burn glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP and produce carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria in Creb cycle.